Introduction

In the realm of aviation, understanding the nuances of FAA RVR is crucial for ensuring safe flight operations. Runway Visual Range (RVR) provides essential information about visibility conditions on runways, which directly impacts pilots' decisions during takeoff and landing. As we delve into the fundamentals of RVR, we will explore its significance in aviation safety and the key elements involved in its measurement.
Understanding FAA RVR Basics
What is the FAA RVR? Simply put, it’s a critical measurement that indicates how far a pilot can see down the runway under various weather conditions. Unlike general visibility, which can be influenced by a variety of factors, FAA RVR focuses specifically on what’s visible from the cockpit to ensure that pilots have accurate information when making landing decisions. This understanding is vital for maintaining flight safety and operational efficiency.
Importance of RVR in Aviation
The importance of RVR in aviation cannot be overstated; it serves as a vital component for safe landings and takeoffs, especially during inclement weather conditions like fog or heavy rain. Accurate readings help determine whether it's safe to proceed with an approach or if conditions warrant holding patterns or diversions to alternate airports. By providing precise data on visibility, FAA RVR plays an indispensable role in minimizing risks associated with low-visibility operations.
Key Elements of RVR Measurement
Key elements involved in measuring FAA RVR include sophisticated technology that assesses atmospheric conditions and runway lighting systems to deliver accurate readings. The process involves using advanced equipment such as Haisen's BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment, which utilizes lasers sensitive to human eyesight wavelengths for precise calculations. Understanding these measurement techniques ensures that pilots receive reliable data regarding what is 2400 RVR in miles and other critical thresholds necessary for safe landings.
What is the FAA RVR?

Understanding the FAA RVR is crucial for pilots, air traffic controllers, and anyone involved in aviation safety. The Runway Visual Range (RVR) provides vital information about visibility conditions on runways, which directly impacts flight operations. By clarifying what FAA RVR is, how it's measured, and its significance in ensuring safe landings and takeoffs, we can appreciate its role in aviation.
Definition of Runway Visual Range
Runway Visual Range (RVR) is a specific measurement used to indicate the distance a pilot can see down the runway during landing or takeoff. Unlike general visibility measurements that might encompass broader areas, RVR focuses solely on the visual range available on runways. This precision makes it an essential metric in aviation safety protocols, helping pilots make informed decisions regarding their approach and landing.
How FAA RVR is Measured
The measurement of FAA RVR typically involves sophisticated equipment designed to assess atmospheric conditions affecting visibility directly along the runway. The BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment from Haisen employs a laser with a wavelength sensitive to human vision as its light source. By analyzing how much this laser's intensity diminishes as it travels through the atmosphere—while considering factors like runway lighting and background brightness—the system accurately determines how far pilots can see runway markers and lights.
Importance of FAA RVR for Flight Safety
The importance of FAA RVR cannot be overstated when it comes to flight safety; it directly influences decision-making during critical phases of flight such as approaches and landings. For instance, knowing whether conditions meet or exceed minimum thresholds for ILS approaches helps ensure that pilots can safely execute landings without risking accidents due to poor visibility. Moreover, accurate RVR readings contribute significantly to overall situational awareness in challenging weather conditions—making them indispensable tools in modern aviation operations.
RVR and Visibility: Are They the Same?

Differences Between RVR and General Visibility
Is RVR the same as visibility? The answer is a resounding no! FAA RVR focuses on specific distances related to runway conditions, providing a more precise measurement critical for instrument approaches. General visibility, on the other hand, considers all atmospheric factors affecting sightlines but doesn't account for runway-specific obstacles or lighting conditions that can impact a pilot's ability to land safely.
This differentiation is vital because pilots rely heavily on accurate FAA RVR readings during low-visibility situations. For example, while general visibility might indicate that it's possible to see several miles away, if the RVR reading is low—say what is 2400 RVR in miles?—it could mean that landing isn't safe at that moment due to obscured runway lights or other critical visual cues.
Use Cases for RVR in Aviation
FAA RVR plays a pivotal role in various aviation scenarios where precision matters most. For instance, during poor weather conditions such as fog or heavy rain, pilots must refer to accurate RVR measurements to determine whether they can safely conduct an approach and landing at their destination airport. This data becomes even more essential when considering what is the minimum RVR for ILS (Instrument Landing System) approaches; regulatory standards dictate specific thresholds that must be met before proceeding with such maneuvers.
Additionally, air traffic controllers use FAA RVR data to make informed decisions about takeoffs and landings at busy airports during adverse weather events. By relying on this specialized measurement rather than general visibility reports alone, they can ensure safer operations while minimizing delays caused by low-visibility conditions.
Impact of RVR on Flight Operations
The impact of FAA RVR on flight operations cannot be overstated; it directly influences safety protocols and operational efficiency in aviation environments. When pilots receive real-time updates regarding their airport's current Runway Visual Range (RVR), they are better equipped to make crucial decisions about whether it's safe to land or if they should divert elsewhere due to insufficient visual cues.
Moreover, understanding variations in FAA RVR helps airlines prepare contingency plans during adverse weather events—ensuring passenger safety remains paramount while optimizing scheduling logistics despite challenging conditions. As technology advances with equipment like Haisen's BHP01 Transmission Measurement Equipment—which utilizes sensitive laser technology—the accuracy of these measurements continues improving, thereby enhancing overall flight safety across global airspace.
Converting RVR Values
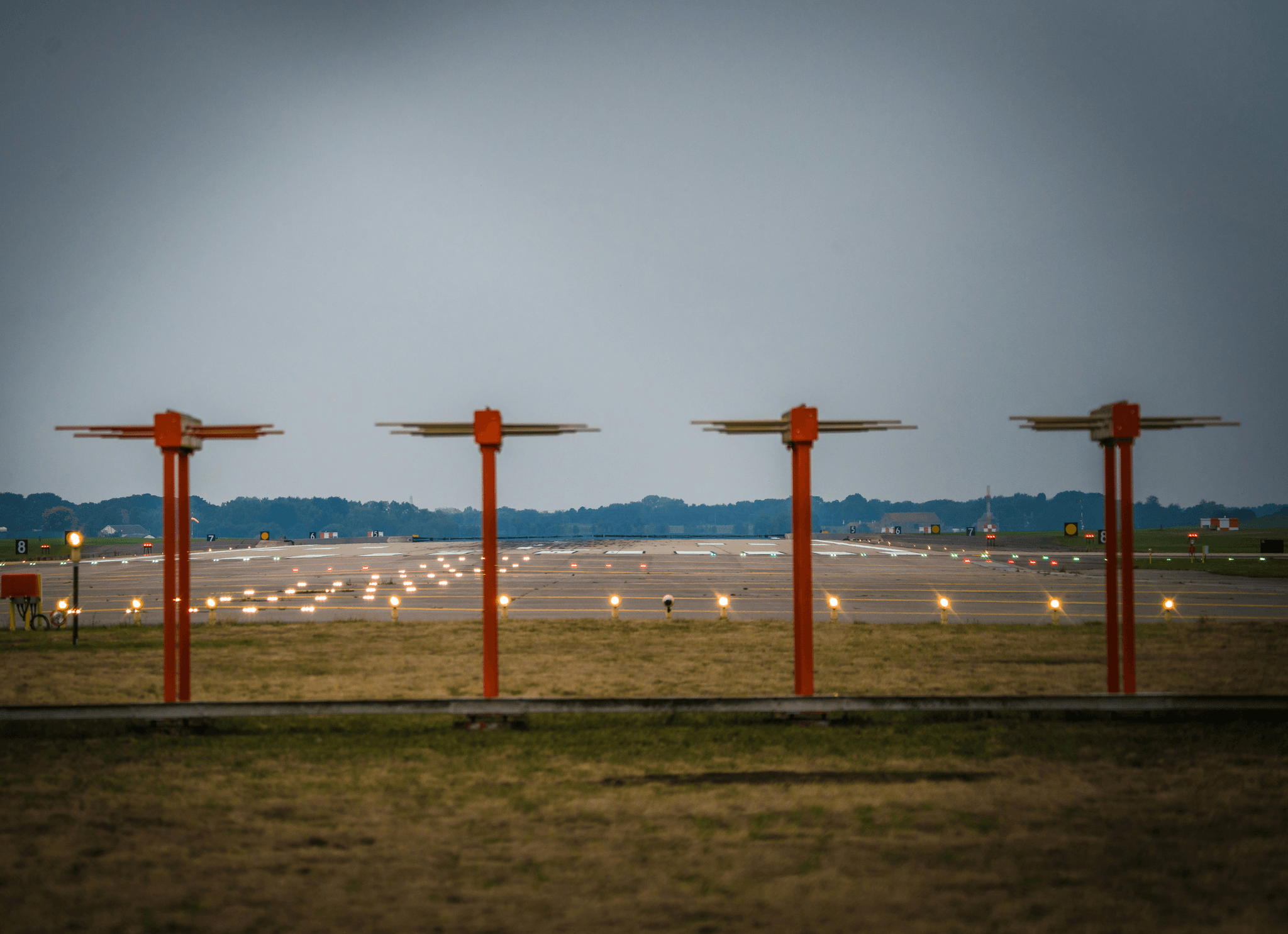
Understanding how to convert RVR values is crucial for pilots and air traffic controllers alike. The FAA RVR system provides a standardized way to measure runway visibility, which directly impacts flight safety. In this section, we will explore what 2400 RVR means in miles, how to interpret these readings effectively, and emphasize the importance of accurate measurements in aviation.
What is 2400 RVR in Miles?
When we talk about What is 2400 RVR in miles?, it's important to note that 2400 feet of Runway Visual Range (RVR) translates roughly to about 0.45 miles. This conversion helps pilots understand visibility conditions on the runway during landing or takeoff operations. For context, when the FAA RVR indicates 2400, it signifies a significant reduction in visibility that can impact flight operations and necessitate careful adherence to minimums.
How to Interpret RVR Readings
Interpreting RVR readings requires an understanding of both the numbers and their implications for flight safety. The FAA measures RVR using advanced systems that calculate how far a pilot can see based on atmospheric conditions and lighting on the runway. For instance, if an airport reports an RVR of less than 1800 feet, it may not be suitable for certain instrument approaches like ILS (Instrument Landing System), raising questions about whether Is RVR the same as visibility?—the answer being no; they are related but distinct metrics.
Importance of Accurate Measurements
Accurate measurements are vital when dealing with FAA RVR readings because they directly influence operational decisions made by pilots and air traffic controllers. If there’s even a slight error in measurement, it could lead to unsafe landing or takeoff situations, especially under low-visibility conditions where every foot counts. Utilizing reliable equipment like Haisen's BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment ensures that these measurements are precise; this system employs advanced laser technology combined with ICAO standards to provide accurate visual range data critical for safe aviation practices.
Minimum RVR for Instrument Approaches

Understanding the minimum RVR for instrument approaches is crucial for ensuring safe landings in adverse weather conditions. The FAA has established specific standards that dictate the minimum required Runway Visual Range (RVR) for various types of landings, particularly for Instrument Landing System (ILS) approaches. This section will clarify what these minimums are and why they matter in aviation safety.
What is the Minimum RVR for ILS?
The minimum RVR required for an ILS approach can vary based on several factors, including the aircraft type and airport category. Generally, the FAA stipulates that a minimum RVR of 1,800 feet is necessary to execute a standard Category I ILS approach safely. Understanding What is the minimum RVR for ILS? helps pilots prepare adequately and ensures compliance with safety regulations during low visibility conditions.
This threshold is critical because it directly impacts flight operations and decision-making processes in challenging weather scenarios. Pilots must be aware of these requirements to maintain situational awareness when planning their approach and landing strategies. Ultimately, adhering to these guidelines enhances overall flight safety.
RVR Thresholds for Safe Landings
RVR thresholds are established not only for ILS approaches but also apply to other types of instrument approaches as well. For example, while 1,800 feet may be sufficient for a standard ILS approach, different thresholds exist depending on whether pilots are using a Localizer Performance with Vertical Guidance (LPV) or other navigational aids. Knowing these distinctions allows flight crews to make informed decisions about alternate routes or diverting when conditions deteriorate.
Additionally, understanding how Is RVR the same as visibility? can help clarify why specific thresholds exist. While general visibility might suggest acceptable flying conditions, it does not always align with actual runway visual ranges measured by instruments like Haisen's BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment. In situations where visibility appears adequate but actual runway visual range falls short, pilots must rely on accurate measurements to ensure safe operations.
Regulatory Standards in Aviation
Regulatory standards set forth by organizations like the FAA provide essential guidelines regarding minimum RVR requirements during instrument approaches. These regulations are designed not only to enhance safety but also to standardize practices across various airports nationwide and internationally. Compliance with these standards ensures that all pilots operate under consistent expectations regardless of their location or aircraft type.
Moreover, advancements in technology have led to improvements in measuring tools such as Runway Visual Range (RVR) systems like Haisen's BHP01 equipment that enhances accuracy in determining visibility ranges on runways effectively. By using sophisticated algorithms based on ICAO standards combined with laser transmission technology, this equipment provides precise measurements crucial for maintaining regulatory compliance during low-visibility operations.
In conclusion, understanding the importance of minimum RVR values helps reinforce best practices among aviation professionals while emphasizing how critical accurate measurements are when navigating through adverse weather conditions.
Haisen's RVR Measurement Equipment

Accurate measurement of Runway Visual Range (RVR) is crucial for ensuring flight safety, especially in low-visibility conditions. One of the leading technologies in this field is Haisen's BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment. This innovative system not only enhances the accuracy of RVR readings but also aids pilots and air traffic controllers in making informed decisions during critical flight operations.
Overview of BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment
The BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment utilizes a laser with a wavelength finely tuned to the sensitivity range of human eyesight, making it an effective tool for measuring FAA RVR. By adhering to ICAO standard algorithms, this equipment measures how much laser light is absorbed or scattered by atmospheric particles, providing precise data on visibility conditions at airports. With components including a laser transmitting end, an optical receiving end, and a remote control unit, it streamlines the process of determining runway visibility.
How Haisen's Equipment Works
Haisen’s equipment operates by sending out a laser beam that interacts with atmospheric conditions as it travels towards runway lights such as boundary lights and centerline lights. The system then calculates how much light reaches the receiving end based on transmission attenuation caused by weather factors like fog or rain—key elements that affect FAA RVR measurements. This sophisticated approach allows for real-time monitoring and automatic calculations of airport runway visual range and airport visibility.
Benefits of Accurate RVR Measurement
The benefits of accurate RVR measurement cannot be overstated; they directly contribute to enhanced safety during takeoffs and landings in challenging weather conditions. With precise data on what is 2400 RVR in miles or what is the minimum RVR for ILS approaches, pilots can make better-informed decisions regarding their landing options. Furthermore, understanding whether Is RVR the same as visibility? helps clarify operational protocols and ensures compliance with regulatory standards in aviation.
Conclusion

As we wrap up our exploration of FAA RVR, it's clear that understanding Runway Visual Range (RVR) is crucial for aviation safety and efficiency. The FAA RVR system plays a pivotal role in ensuring pilots have the necessary information to make informed decisions during approaches and landings in varying visibility conditions. With precise measurements, such as what is 2400 RVR in miles, pilots can gauge their operational limits and enhance safety protocols.
Recap on FAA RVR Significance
The significance of FAA RVR cannot be overstated; it serves as a critical tool for assessing runway conditions and visibility during flight operations. By providing accurate metrics on what is the minimum RVR for ILS approaches, it helps pilots determine whether it’s safe to land or if they should divert to an alternate airport. Additionally, understanding whether Is RVR the same as visibility allows for clearer communication among air traffic controllers and flight crews, ensuring everyone is on the same page when it comes to safety.
Final Thoughts on RVR and Safety
In conclusion, the relationship between RVR Aviation metrics and flight safety is undeniable. Accurate readings of Runway Visual Range (RVR) can mean the difference between a safe landing and a potential mishap during adverse weather conditions. As we continue to refine our understanding of aviation visibility standards, embracing technologies like Haisen's BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment will only enhance our ability to maintain high safety standards in increasingly complex flying environments.
Future of RVR in Aviation Technology
Looking ahead, the future of FAA RVR technology holds exciting possibilities that could revolutionize how we approach aviation safety measures. Innovations such as enhanced laser systems for measuring visibility will provide even more reliable data for pilots navigating challenging conditions. As we strive for greater accuracy in determining metrics like what is 2400 RVR in miles or establishing new benchmarks for minimum requirements like what is the minimum RVR for ILS, advancements will undoubtedly lead us toward safer skies.
