Introduction
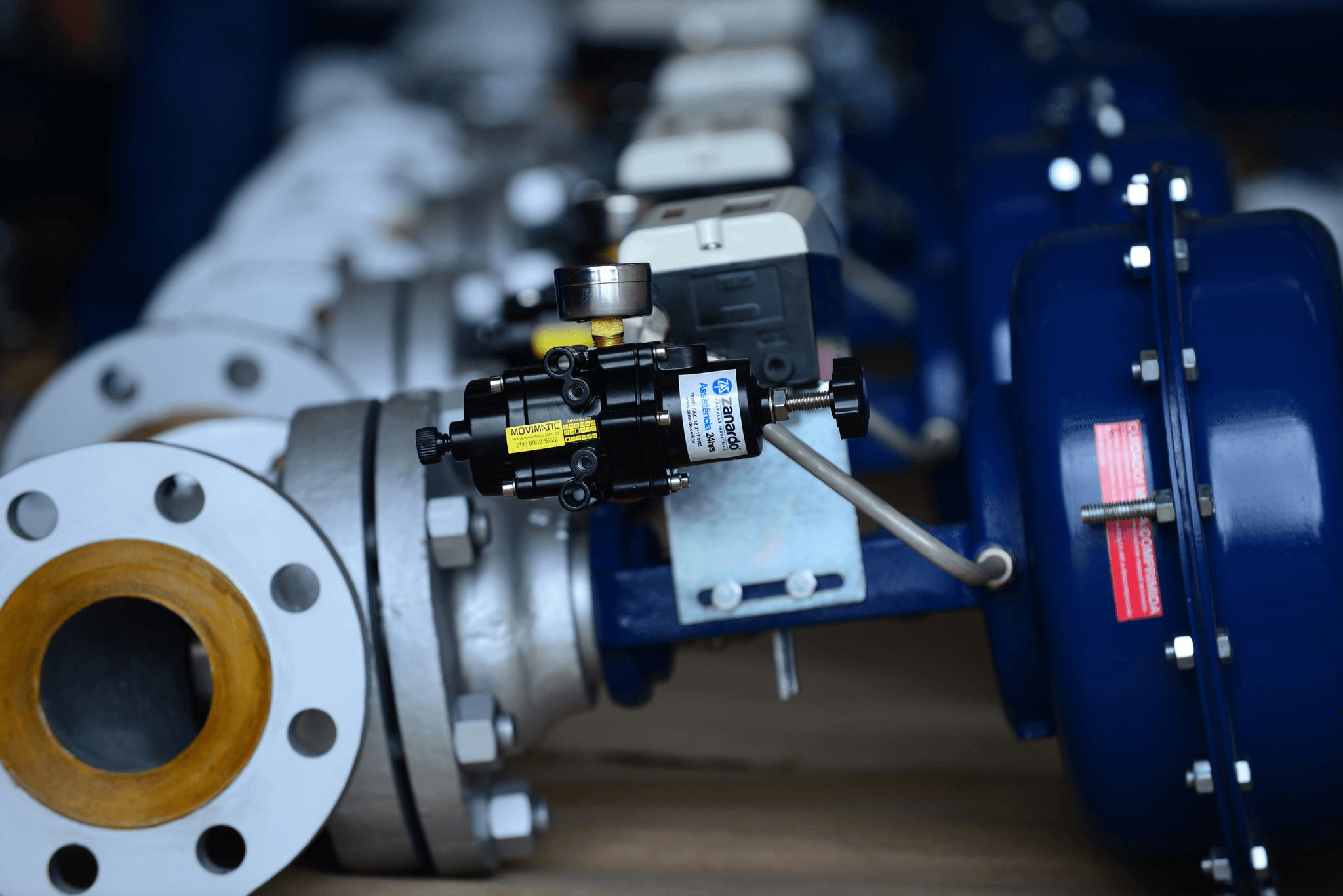
When it comes to controlling fluid flow in various industrial applications, valve actuators play a critical role. These devices are the unsung heroes behind the scenes, translating control signals into mechanical movement to operate valves effectively. Understanding valve actuators is essential for anyone involved in system design or maintenance, as their performance directly impacts operational efficiency and safety.
Understanding Valve Actuators
At its core, an actuator in a valve is a device that converts energy into motion, specifically designed to open or close valves based on control signals. This functionality is crucial for managing processes across different industries, from petrochemicals to food production. By grasping what an actuator in a valve does, engineers can better select the right type for their specific needs.
Importance of Selecting the Right Actuator
Choosing the right actuator can significantly affect not only system performance but also cost-effectiveness and reliability. With various types available—each with unique characteristics—understanding what are the 3 most common actuators can guide decision-making processes. Selecting an appropriate actuator ensures optimal operation and minimizes downtime due to equipment failures.
Overview of Actuator Types
There are primarily three types of actuators: electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic, each suited for different applications and environments. Electric actuators offer precision control and ease of integration with electronic systems; pneumatic actuators provide rapid response times; while hydraulic actuators excel in high-force applications. Additionally, understanding concepts like quarter turn actuators versus part turn actuators further refines choices based on specific operational requirements.
What is an Actuator in a Valve?

Valve actuators are essential components that play a crucial role in the operation of valves within various systems. They serve as the driving force that opens or closes the valve, allowing for precise control over fluid flow. Understanding what an actuator in a valve is can help streamline processes and improve efficiency across numerous industries.
Definition and Functionality
An actuator in a valve is a device that converts energy into mechanical motion to operate the valve mechanism. This functionality allows it to either open or close the valve, depending on system requirements. Without actuators, valves would remain stationary, rendering them ineffective for regulating flow and pressure.
The primary purpose of these devices is to provide automation and remote control capabilities, which enhances operational efficiency in industrial applications. By employing different types of actuators—electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic—users can achieve varying degrees of responsiveness and power based on their specific needs. Ultimately, understanding what an actuator in a valve does is fundamental for anyone involved in fluid dynamics or process engineering.
Key Components of Valve Actuators
Valve actuators consist of several key components that work together to perform their functions effectively. These include the motor (in electric actuators), air supply (in pneumatic models), and hydraulic fluid (in hydraulic types). Each component contributes to translating energy into mechanical motion that operates the valve.
Additionally, many actuators incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to monitor position and performance accurately. This enables real-time adjustments based on system demands, ensuring optimal operation under varying conditions. Recognizing these components can help users select appropriate actuators for their specific applications.
Common Applications
Valve actuators find widespread use across diverse industries due to their versatility and efficiency. Common applications include controlling water flow in municipal systems, regulating pressure in oil pipelines, and managing chemical processes in manufacturing plants. Their ability to automate operations significantly reduces manual labor while enhancing safety.
In sectors like petrochemical refining or food processing, precise control over valves ensures compliance with regulatory standards while maintaining product quality. Moreover, quarter turn actuators are particularly favored for their simplicity and effectiveness when dealing with valves requiring 90° rotation—such as butterfly valves or ball valves—making them indispensable tools across multiple domains.
Haisen's QT series part-turn valve electric actuator exemplifies this trend by offering reliable performance tailored for various industrial needs. Its design supports local or remote operation for controlling butterfly valves, ball valves, and plug valves efficiently across numerous fields including metallurgy and construction.
What Are the 3 Most Common Actuators?
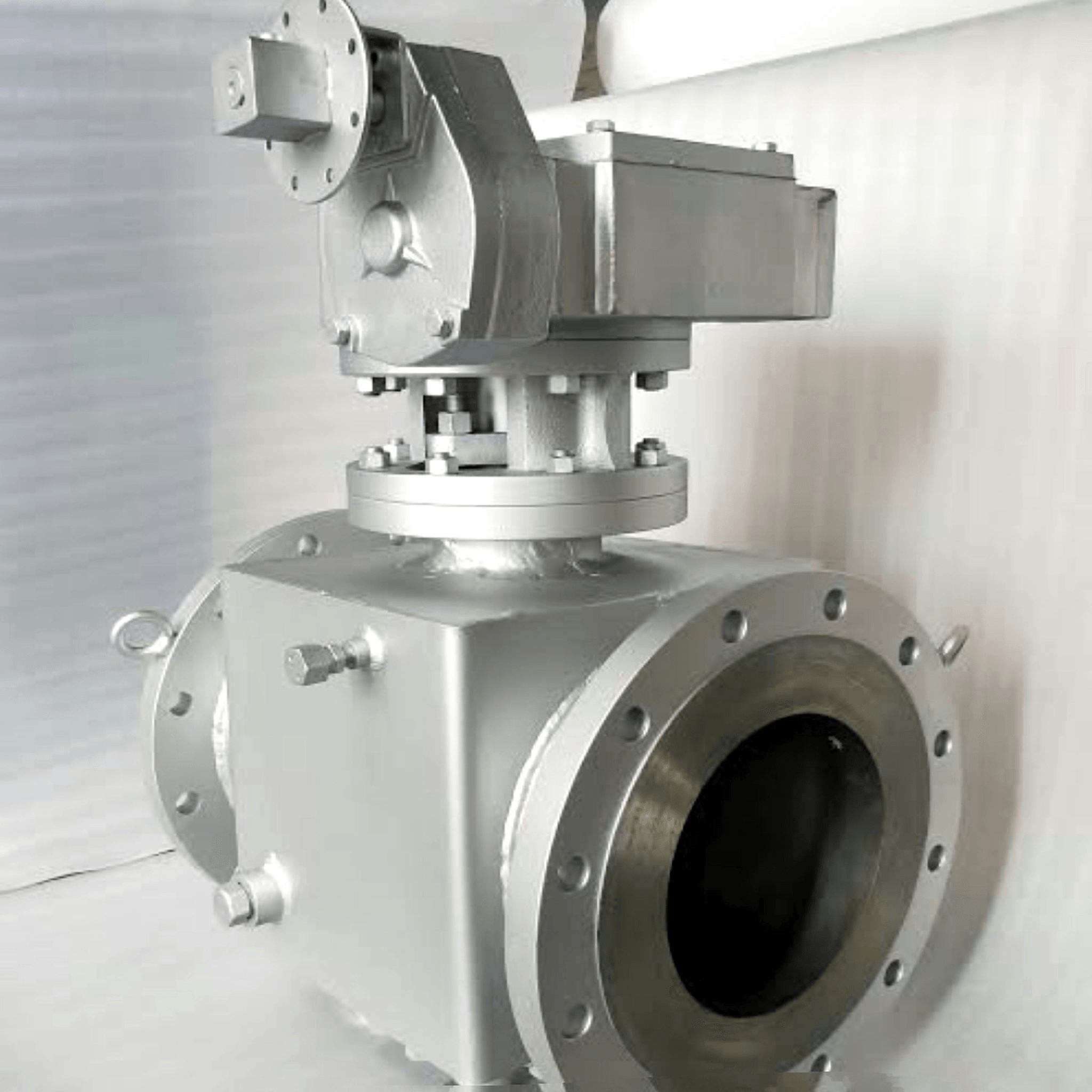
When discussing valve actuators, it’s essential to recognize that there are three primary types that dominate the industry: electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications, making them suitable for different environments and requirements. Understanding these common actuators can help you make informed decisions regarding what is an actuator in a valve.
Electric Actuators
Electric actuators are powered by electricity and are known for their precision and ease of control. They convert electrical energy into mechanical motion to operate valves effectively. These valve actuators are particularly favored in applications requiring accurate positioning and minimal maintenance, making them ideal for industries like food processing and water treatment.
One of the significant advantages of electric actuators is their ability to be integrated with automation systems effortlessly, allowing for remote monitoring and control. This feature enhances operational efficiency while reducing the need for manual intervention. Furthermore, electric actuators are often quieter than their pneumatic counterparts, which is a crucial factor in settings where noise reduction is necessary.
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to generate motion, making them powerful tools for quickly opening or closing valves. These valve actuators excel in environments where rapid actuation is crucial, such as in chemical processing or manufacturing lines that require swift responses to changes in pressure or flow rates. The simplicity of pneumatic systems often leads to lower initial costs compared to electric options.
However, pneumatic actuators do require an air supply system which can complicate installation and maintenance procedures. Additionally, they may not provide as precise control as electric actuators but can still be highly effective in applications where speed trumps accuracy. In summary, when asking what are the 3 most common actuators? Pneumatic options certainly hold a prominent place due to their reliability and performance.
Hydraulic Actuators
Hydraulic actuators operate by using pressurized fluid to create motion, providing immense force with relatively compact designs—ideal for heavy-duty applications like mining or large-scale manufacturing processes involving massive valves. These valve actuators deliver high torque output without requiring large physical sizes compared to other actuator types; this makes them suitable when space constraints exist.
Moreover, hydraulic systems can maintain force over extended periods without needing continuous power input—an excellent feature for applications requiring sustained operation under load conditions without frequent adjustments or interventions. However, hydraulic systems may entail higher maintenance due to potential leaks and require careful handling of fluids involved.
In conclusion, understanding the differences among these three common actuator types—electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic—is vital when selecting components for your system's needs related to what is the difference between valve actuator and positioner? Each actuator type has unique advantages suited for specific tasks across various industries.
Comparing Valve Actuator and Positioner
When it comes to the functionality of valve actuators, understanding the role of positioners is crucial. Positioners enhance the performance of valve actuators by ensuring that they reach the desired position accurately and efficiently. This synergy between actuator and positioner is vital for achieving optimal control in various industrial applications.
Definition and Purpose of Positioners
Positioners are devices designed to control the movement of valve actuators, ensuring that they operate at precise angles or positions as required by a process. They receive signals from control systems that dictate how far a valve should open or close, translating these signals into mechanical action for the actuator. In essence, positioners act as the brain behind valve actuators, allowing for more precise control over fluid flow in pipelines.
How They Work Together
The relationship between valve actuators and positioners can be likened to a dance; they must work seamlessly together to achieve their goals. When a control signal is sent, the positioner interprets this data and sends commands to the actuator to adjust its position accordingly. This collaboration not only improves response times but also enhances overall system reliability, making it easier to maintain desired process conditions across various applications.
Importance in Industrial Applications
In industrial settings where precision is paramount, understanding what is the difference between valve actuator and positioner can significantly impact operational efficiency. The integration of these two components allows for higher accuracy in controlling flow rates, which is essential in industries such as petrochemical processing or thermal power generation. By optimizing performance through this partnership, businesses can reduce waste, improve safety measures, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
The Difference Between Valve Body and Actuator
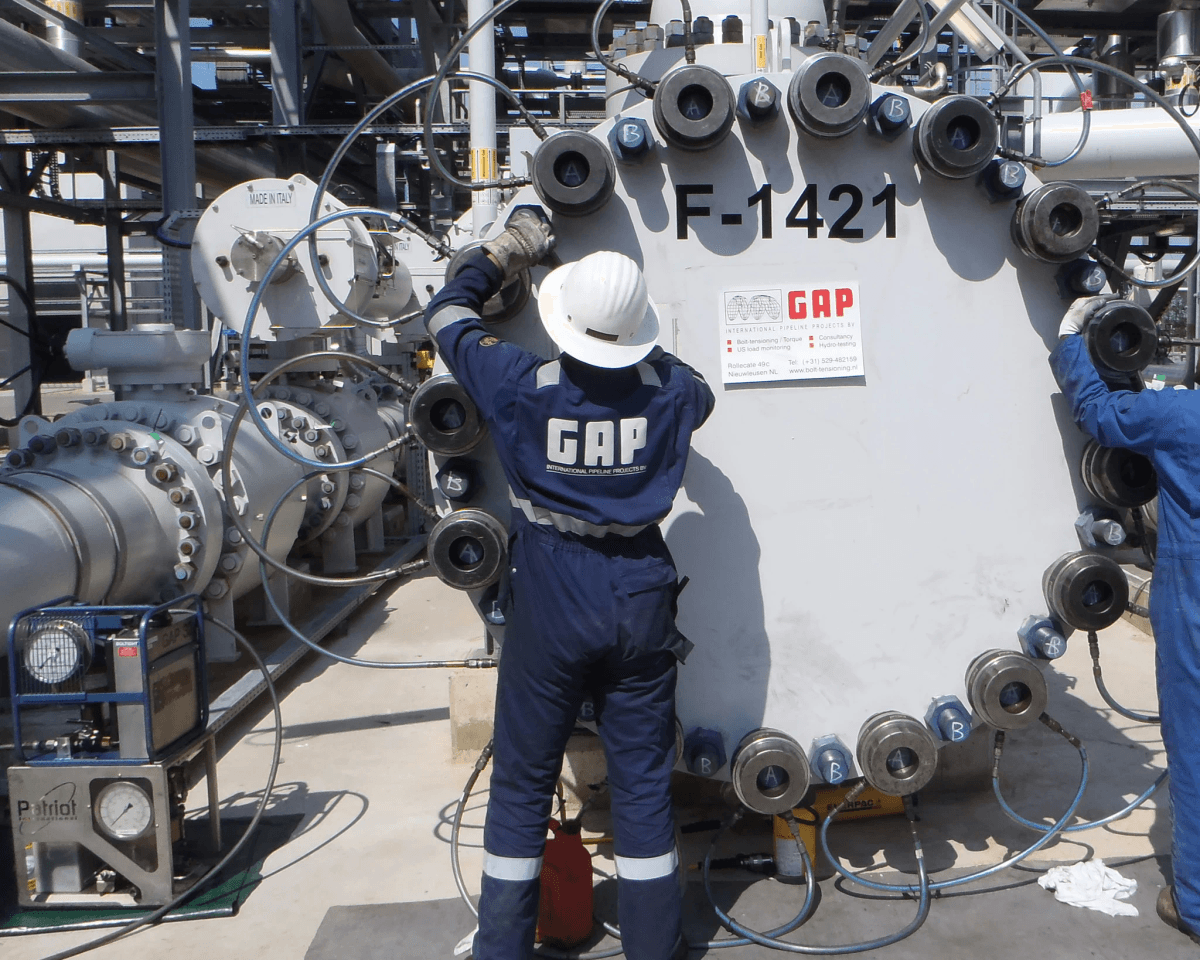
When delving into the world of valve technology, it’s crucial to understand the distinct roles played by the valve body and actuator. While both components work in tandem to control fluid flow, they serve different purposes within a system. This section will clarify these differences, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of what is an actuator in a valve and its relationship with the valve body.
Understanding Valve Design
Valve design revolves around creating efficient systems that control the flow of liquids or gases through pipelines. The valve body is essentially the structure that houses various internal components like seats, seals, and discs, all designed to regulate flow effectively. In contrast, when we talk about what is an actuator in a valve?, we refer specifically to the mechanism responsible for moving these internal components based on external commands.
The integration of these two elements—valve body and actuator—is vital for effective operation in various applications. Understanding how they interact can help engineers select appropriate components for specific tasks. This knowledge also aids in troubleshooting issues that may arise during operation.
Role of the Actuator
The actuator plays a pivotal role in translating control signals into physical movement within the valve system. Essentially, it converts energy—whether electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic—into mechanical motion that opens or closes the valve body as needed. Without an effective actuator, even the most sophisticated valve design would be rendered ineffective.
In essence, while valves can be engineered with high precision to manage flow rates optimally, their functionality hinges on reliable actuators to execute those designs accurately. When considering what are the 3 most common actuators?, it's essential to note that each type has unique advantages suited for different operational contexts within industrial settings.
Features and Characteristics
Valve bodies typically feature durable materials designed to withstand high pressures and corrosive environments; they are often made from metals like stainless steel or brass depending on application needs. On the other hand, actuators come equipped with features such as torque output ratings and response times tailored for specific operational demands—these characteristics determine how quickly and effectively they can operate valves under varying conditions.
Additionally, quarter turn actuators are particularly noteworthy due to their ability to facilitate rapid opening or closing actions over short rotational distances—ideal for applications involving butterfly valves or ball valves where speed is essential. Haisen's QT series part-turn valve electric actuator exemplifies this efficiency; it's developed based on existing technologies while enhancing performance across numerous industries including petrochemical and food processing sectors.
In conclusion, understanding what is the difference between valve body and actuator allows for better decision-making when selecting components for your system needs. By recognizing their respective roles and features within industrial applications—including how they complement one another—you'll be well-equipped to optimize fluid control solutions effectively.
Exploring Quarter Turn Actuators
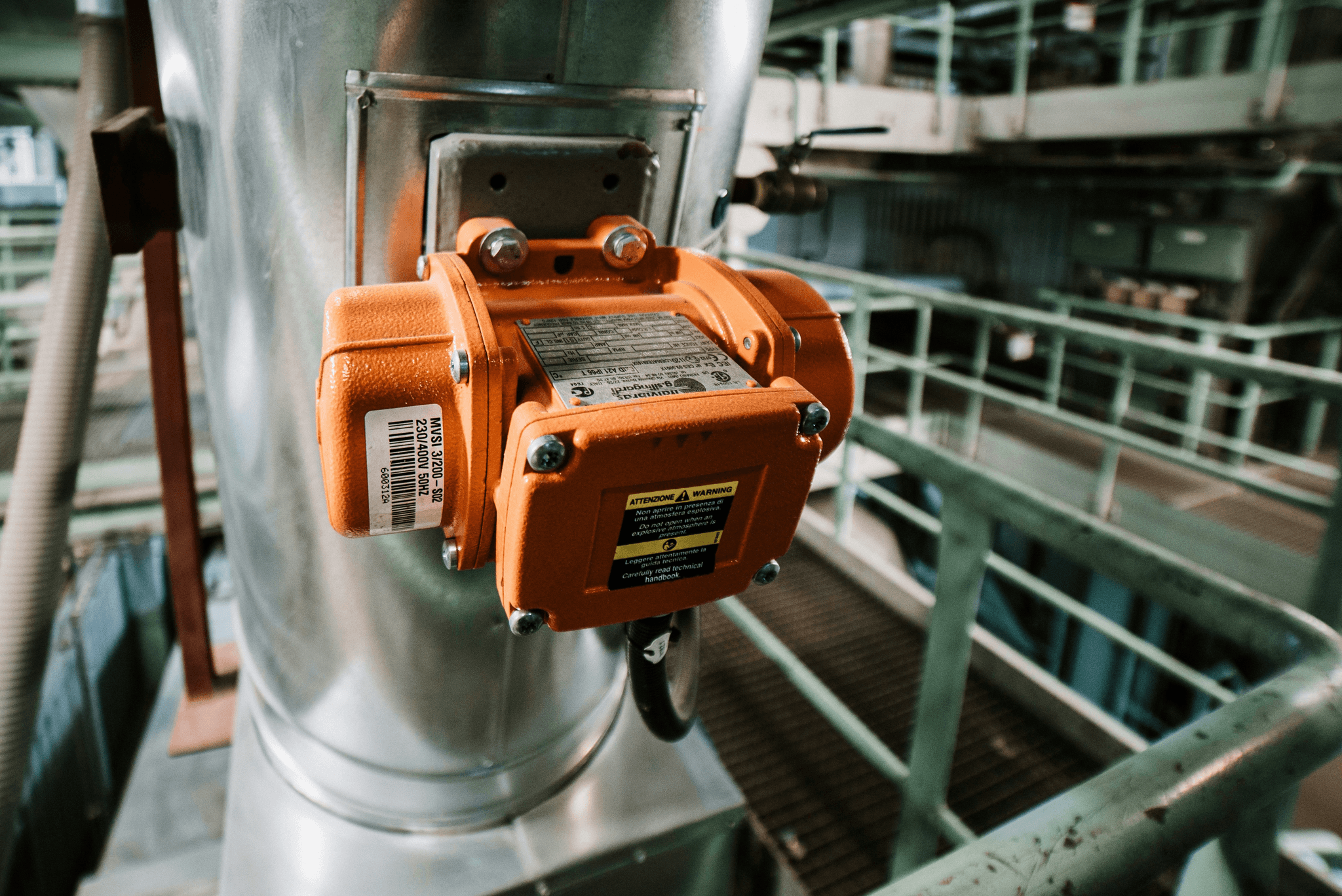
Quarter turn actuators are essential components in valve systems, providing precise control for various types of valves. These actuators are designed to rotate a valve by 90 degrees, making them ideal for applications where quick on/off functionality is required. Understanding the mechanism and operation of quarter turn actuators is crucial for selecting the right actuator for specific industrial needs.
Mechanism and Operation
The mechanism of quarter turn actuators typically involves a simple yet effective design that transforms rotary motion into linear movement to open or close valves. This operation is achieved through gears and motors that work together seamlessly to ensure smooth transitions. When considering what an actuator in a valve does, it’s clear that these devices are vital for controlling fluid flow with minimal effort.
Quarter turn actuators can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic, each offering unique advantages depending on the application requirements. Electric actuators utilize electrical energy to drive motors, while pneumatic ones rely on compressed air; hydraulic actuators use pressurized fluid to create movement. Understanding the three most common actuators helps users choose the best type based on their operational environment and energy availability.
Applications in Different Industries
Quarter turn actuators find applications across various industries due to their versatility and efficiency in controlling valves like ball valves and butterfly valves. In petrochemical plants, these actuators enable rapid response times crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency during operations. Similarly, industries such as food processing, construction, and thermal power also benefit from these reliable devices.
Their ability to provide quick actuation makes them suitable for environments where time-sensitive operations are critical—think about municipal engineering projects requiring immediate responses during emergencies or maintenance activities. Furthermore, quarter turn actuators play a significant role in shipbuilding by ensuring proper control over ballast systems and other essential functions aboard vessels.
Haisen's Part-Turn Valve Electric Actuator
Haisen's QT series part-turn valve electric actuator represents an innovative leap in actuator technology tailored specifically for various industrial applications. This product is designed based on extensive research into both domestic and international standards, ensuring it meets diverse operational needs effectively. It excels at controlling butterfly valves, ball valves, and plug valves with its efficient 90° rotation capability.
One of the standout features of Haisen's part-turn actuator is its flexibility; it can be operated locally or remotely controlled depending on user preference or operational requirements. This adaptability makes it particularly appealing in industries such as metallurgy or hydropower where remote monitoring can enhance productivity while maintaining safety protocols. With its robust design tailored for pipeline valve control across multiple sectors—including food production and construction—Haisen’s actuator exemplifies modern advancements in valve technology.
Conclusion

In the world of industrial automation, selecting the right valve actuators is crucial for ensuring efficient operation and reliability. Understanding the nuances of what is an actuator in a valve can help streamline processes, enhance safety, and improve overall system performance. With various options available, including electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic types, it’s essential to make an informed choice that aligns with specific application needs.
Choosing the Right Type of Valve Actuator
When it comes to choosing valve actuators, one must consider the operational requirements and environmental conditions they will face. The three most common actuators—electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic—each have unique advantages that cater to different scenarios. For instance, electric actuators are ideal for precise control in applications requiring minimal maintenance, while pneumatic actuators excel in environments where rapid response times are critical.
Key Considerations for Selection
Selecting the right actuator involves assessing several key factors such as torque requirements, speed of operation, and compatibility with existing systems. Understanding what is the difference between valve actuator and positioner also plays a role; while actuators provide movement to valves based on signals received from controllers or positioners fine-tune that movement for optimal performance. Additionally, considering what is the difference between valve body and actuator can help clarify how these components work together to achieve desired functionality.
Future Trends in Actuator Technology
The future of actuator technology looks promising with advancements aimed at enhancing efficiency and sustainability across industries. Innovations such as smart actuators equipped with IoT capabilities are emerging trends that allow real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance features to be integrated into valve systems. As industries increasingly adopt automation solutions like Haisen's QT series part-turn valve electric actuator—which offers versatile control over various valves—it's clear that staying updated on trends in valve actuators will be essential for maintaining competitive advantages.
