Introduction

In the world of aviation, understanding Runway Visual Range (RVR) is essential for ensuring safe and efficient flight operations. RVR serves as a critical metric that provides pilots with crucial information about visibility conditions on the runway. By grasping the significance of RVR in aviation, we can appreciate its role in enhancing safety and optimizing flight planning.
Understanding the Importance of RVR
What is a RVR in aviation? Simply put, it quantifies how far a pilot can see along the runway, which is vital during takeoff and landing phases when visibility may be compromised due to weather conditions. Accurate RVR readings help pilots make informed decisions about whether to proceed with landing or takeoff, significantly influencing operational safety at airports.
The Role of RVR in Aviation Safety
The role of RVR in aviation safety cannot be overstated; it directly impacts how flights are managed during low-visibility situations. When pilots are aware of what does 2400 RVR mean—indicating a visibility range of 2400 feet—they can adjust their approach accordingly to ensure a safe landing or departure. Furthermore, understanding the FAA definition of RVR helps standardize procedures across different airports, contributing to overall air traffic safety.
Key Terms and Definitions in RVR
To navigate discussions around Runway Visual Range effectively, familiarity with key terms is necessary. Is RVR the same as visibility? While both measure how much one can see, they serve different purposes within aviation contexts—RVR focuses on runway conditions specifically while general visibility encompasses broader atmospheric clarity. Additionally, knowing how Runway Visual Range (RVR) works—including its measurement techniques and equipment like Haisen's BHP01 Transmission System—provides deeper insights into its practical applications for pilots and air traffic controllers alike.
What is RVR and Its Significance

Runway Visual Range (RVR) is a crucial metric in aviation, providing pilots with vital information about visibility conditions on the runway. Understanding what RVR is and its significance can enhance safety during takeoff and landing operations. In this section, we will define RVR, explore its role in aviation, and discuss its importance for both pilots and airports.
Definition of Runway Visual Range
Runway Visual Range (RVR) refers to the distance a pilot can see down the runway, which is critical for safe aircraft operations. Essentially, it measures how far a pilot can see the runway markings or lights under specific weather conditions. The FAA defines RVR as a measurement that reflects the horizontal distance over which pilots can clearly identify runway features at night or during low visibility situations.
RVR in the Context of Aviation
In aviation, RVR plays an essential role in ensuring safe flight operations by providing accurate visibility measurements that inform pilots about current conditions on the runway. It helps determine whether an aircraft can safely take off or land based on established minimum visibility criteria set by regulatory authorities like the FAA. This makes understanding What is a RVR in aviation? crucial for all stakeholders involved in flight operations.
Importance for Pilots and Airports
For pilots, knowing how Runway Visual Range (RVR) works allows them to make informed decisions regarding takeoff and landing procedures under varying weather conditions. Accurate RVR reporting ensures that airports maintain safety protocols while allowing flights to operate efficiently even when visibility is compromised. Moreover, airports rely on precise RVR values to manage traffic flow effectively and minimize delays during adverse weather scenarios.
How Runway Visual Range (RVR) Works

Understanding how Runway Visual Range (RVR) works is crucial for ensuring safe aviation operations. RVR provides pilots with critical information about visibility conditions on the runway, which directly impacts their ability to take off and land safely. This section will delve into the mechanics behind RVR measurement, the essential equipment used, and a closer look at Haisen's innovative RVR measurement technology.
The Mechanics Behind RVR Measurement
At its core, RVR is a measure of how far a pilot can see down the runway under specific weather conditions. It takes into account factors such as fog, rain, snow, or other visibility-reducing phenomena that can significantly affect flight operations. Understanding what is a RVR in aviation involves recognizing that it specifically measures the distance at which runway lights or markings are visible to pilots rather than general atmospheric visibility.
The methodology for calculating RVR often involves using sophisticated instruments that assess light transmission through various atmospheric conditions. By measuring how much light from runway lights is scattered or absorbed by particulates in the air, these instruments can provide an accurate reading of visual range. This precision is vital because knowing whether it's 2400 RVR or less can determine if a flight can proceed safely.
RVR Equipment and Its Role
RVR equipment plays an indispensable role in measuring and reporting visibility on runways effectively. These devices are strategically installed around airports to continuously monitor environmental conditions and relay critical data to air traffic controllers and pilots alike. Notably, understanding when is RVR reported in METAR helps pilots make informed decisions during flight planning based on real-time data.
The equipment typically uses laser technology or other optical methods to gauge visibility accurately over short distances—specifically along runways where precision is paramount for safety during takeoff and landing procedures. The FAA definition of RVR emphasizes that these measurements are distinct from general visibility readings because they focus solely on what pilots need to see when approaching or departing from an airport.
Haisen's RVR Measurement Equipment Explained
Haisen's BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment exemplifies cutting-edge technology in this field. This system employs a recognized laser with the most sensitive wavelength for human eyes as its transmission light source, ensuring optimal performance even under challenging visibility conditions. By utilizing ICAO standard algorithms, it measures transmission attenuation of laser light through the atmosphere while factoring in ambient light levels at airports.
The BHP01 system comprises three main components: a laser transmitting end, an optical receiving end, and a remote control unit that allows operators to monitor measurements effortlessly from afar. This sophisticated setup enables automatic assessments of visual range along airport runways while providing real-time feedback on atmospheric conditions affecting rvr aviation operations overall. With such advanced equipment at their disposal, airports can ensure compliance with safety standards while enhancing operational efficiency.
RVR vs. Visibility: What's the Difference?

When discussing RVR in aviation, it’s crucial to differentiate between Runway Visual Range (RVR) and general visibility. RVR specifically measures how far a pilot can see down the runway, while visibility refers to how far one can see in any direction. Understanding this distinction is vital for safe flight operations, as both metrics influence decision-making during takeoff and landing.
FAA Definition of RVR
The FAA defines RVR as the distance a pilot can see along the runway, determined using specialized equipment that provides an accurate measurement in specific conditions. This definition emphasizes the importance of precise data for ensuring safety during low-visibility situations, especially when weather conditions deteriorate unexpectedly. The FAA’s standards for reporting RVR are critical for pilots and air traffic controllers to maintain safe operations in challenging environments.
How is RVR Different from Visibility?
While both RVR and visibility are concerned with how well a pilot can see, they measure different aspects of visual perception in aviation contexts. Visibility generally accounts for atmospheric conditions affecting sight over longer distances, while RVR focuses on specific measurements relevant to runway operations. Therefore, it’s possible for an airport to have good overall visibility but poor RVR due to localized fog or precipitation impacting only the runway area.
Implications for Flight Operations
The differences between RVR and visibility have significant implications for flight operations and safety protocols at airports worldwide. For instance, if pilots know that their airport has a reported 2400 RVR but poor overall visibility due to fog elsewhere, they might prepare differently than if both metrics were favorable. Moreover, understanding these nuances helps crews make informed decisions about takeoffs and landings under varying weather conditions—keeping safety at the forefront of aviation practices.
Decoding RVR Values: What Does 2400 RVR Mean?
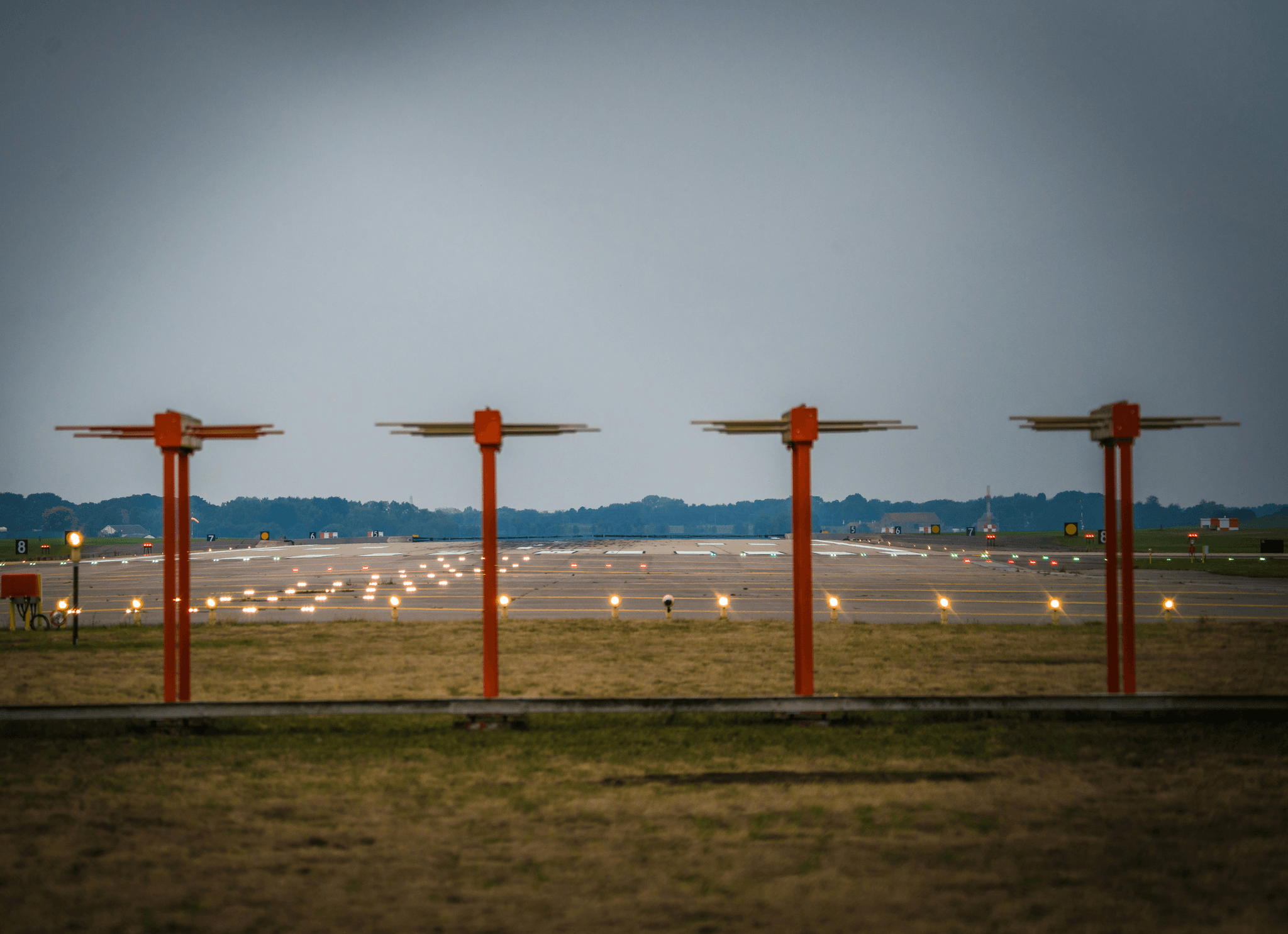
Understanding Runway Visual Range (RVR) values is crucial for pilots and air traffic control alike. When we refer to 2400 RVR, we're discussing a specific measurement that indicates the distance over which a pilot can see runway markings or lights. This value plays a significant role in determining whether flight operations can proceed safely under current weather conditions.
Understanding RVR Values and Thresholds
RVR values are expressed in feet or meters, with thresholds set by aviation authorities like the FAA. For example, 2400 RVR means that pilots can see runway lights or markings clearly up to 2400 feet down the runway. The FAA definition of RVR considers these measurements essential for maintaining safe takeoff and landing procedures, especially in low-visibility conditions.
Different airports may have varying thresholds for acceptable RVR levels based on their specific operational needs and aircraft types. Generally, an RVR of 2400 is considered marginally acceptable for many commercial flights but may require additional precautions during takeoff and landing phases. Understanding these values helps pilots make informed decisions about flight safety when visibility is compromised.
Real-World Applications of Specific RVR Values
In practical terms, what does 2400 RVR mean for aviation operations? When this value is reported, it informs pilots about the current visibility conditions at an airport, impacting their approach strategies and decision-making processes. For instance, if a pilot sees that the reported RVR is at this level, they may opt to use instrument approaches rather than visual ones.
Air traffic controllers also rely on these measurements to manage air traffic efficiently during low-visibility situations. They coordinate with pilots to ensure safe spacing between aircraft during both takeoff and landing phases when visibility might not be ideal. Thus, understanding how Runway Visual Range (RVR) works becomes critical not just for individual flights but also for overall air traffic safety.
Impact on Takeoff and Landing Procedures
The impact of specific RVR values like 2400 on takeoff and landing procedures cannot be overstated in aviation safety discussions. Pilots must adhere strictly to Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) that dictate actions based on reported RVR levels—this includes decisions about whether to proceed with a flight or divert due to inadequate visibility conditions.
For example, if the reported RVR drops below certain thresholds during approach or landing phases—say below 1800 feet—it could trigger missed approaches or go-arounds as part of standard safety protocols. Additionally, airlines may implement stricter requirements regarding crew training and equipment checks when operating under such conditions; thus emphasizing the importance of accurate reporting mechanisms like METAR reports.
In conclusion, understanding what does 2400 RVR mean involves recognizing its significance in real-world applications within aviation practices while adhering to stringent safety measures dictated by regulatory bodies like the FAA.
When is RVR Reported in METAR?

Runway Visual Range (RVR) plays a crucial role in aviation safety, and its reporting is essential for pilots and air traffic controllers alike. Understanding when RVR is reported in METAR (Meteorological Aerodrome Report) provides insights into flight operations during adverse weather conditions. This section will delve into the nuances of RVR reporting, enhancing our grasp of what it means for aviation safety.
Deciphering METAR Reports
METAR reports are standardized aviation weather reports that convey critical information about current weather conditions at airports. Within these reports, RVR values are often included to inform pilots about visibility along the runway, which directly impacts decisions regarding takeoff and landing. For instance, if you're wondering What is a RVR in aviation?, it refers to the distance a pilot can see down the runway, which is vital for safe operations.
When reading METARs, you'll typically see RVR values expressed in meters or feet following specific notations. A report might state RVR 2400, indicating that the visibility along the runway is 2400 meters. Recognizing these details helps pilots assess whether they have sufficient visibility for safe flight operations.
RVR Reporting Protocols and Standards
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has established guidelines dictating when and how RVR should be reported in METARs. According to the FAA definition of RVR, measurements are taken when visibility falls below certain thresholds—usually at 1 statute mile or less—ensuring that pilots receive timely updates on potentially hazardous conditions. These protocols are crucial because they standardize how information is communicated across different airports and regions.
In addition to routine reporting during low-visibility conditions, specific criteria must be met before an airport can report RVR values as part of its regular METAR output. For instance, if there’s significant fog or snow reducing visibility on approach paths, you can expect to see detailed RVR readings included alongside other meteorological data such as wind speed and temperature.
Importance for Flight Planning
Understanding when RVR is reported in METAR significantly impacts flight planning processes for airlines and individual pilots alike. Accurate assessment of Runway Visual Range allows flight crews to determine whether they can safely conduct operations given current weather conditions—especially under scenarios where Is RVR the same as visibility? becomes a pertinent question; it’s not! While both metrics relate to how well one can see, they serve different purposes in operational contexts.
For example, if you encounter an METAR indicating a low 1200 ft visibility but with an accompanying 2400 RVR value due to illuminated runway lights enhancing visual cues at night or during inclement weather—this distinction becomes essential for making informed decisions about landing approaches or alternate routing strategies. Therefore, understanding these metrics helps ensure passenger safety while optimizing operational efficiency within busy airspace systems.
Conclusion

In the world of aviation, understanding Runway Visual Range (RVR) is not just a technicality; it’s a lifeline. RVR plays a critical role in ensuring safe takeoffs and landings, particularly in adverse weather conditions where visibility is compromised. As we’ve explored throughout this discussion, grasping what RVR means and its implications can significantly enhance flight safety for pilots and passengers alike.
The Critical Role of RVR in Aviation
What is a RVR in aviation? It’s not merely a number; it’s an essential measurement that helps pilots gauge whether they can safely land or take off from an airport. The FAA definition of RVR emphasizes its importance as it quantifies how far ahead pilots can see runway markings and lights, which is crucial during low visibility situations. Without accurate RVR readings, the risk of mishaps increases dramatically, making it vital for airports to maintain high standards in measuring and reporting these values.
Safety Enhancements Through Accurate RVR Reporting
Safety enhancements through accurate RVR reporting are paramount for modern aviation operations. When is RVR reported in METAR? This information provides real-time data that allows flight crews to make informed decisions based on current conditions at their destination or alternate airports. Furthermore, understanding what does 2400 RVR mean helps pilots recognize when they are approaching minimums for landing or takeoff, thus enhancing overall safety protocols.
Future of RVR Technology in Aviation
The future of RVR technology in aviation looks promising as advancements continue to improve accuracy and reliability. Haisen's BHP01 Transmission RVR Measurement Equipment exemplifies this evolution by utilizing laser technology to provide precise measurements based on atmospheric conditions and runway lighting. As we push forward into an era where automation and data integration become standard practice, the role of sophisticated RVR equipment will undoubtedly expand, further solidifying its place as a cornerstone of safe aviation practices.
